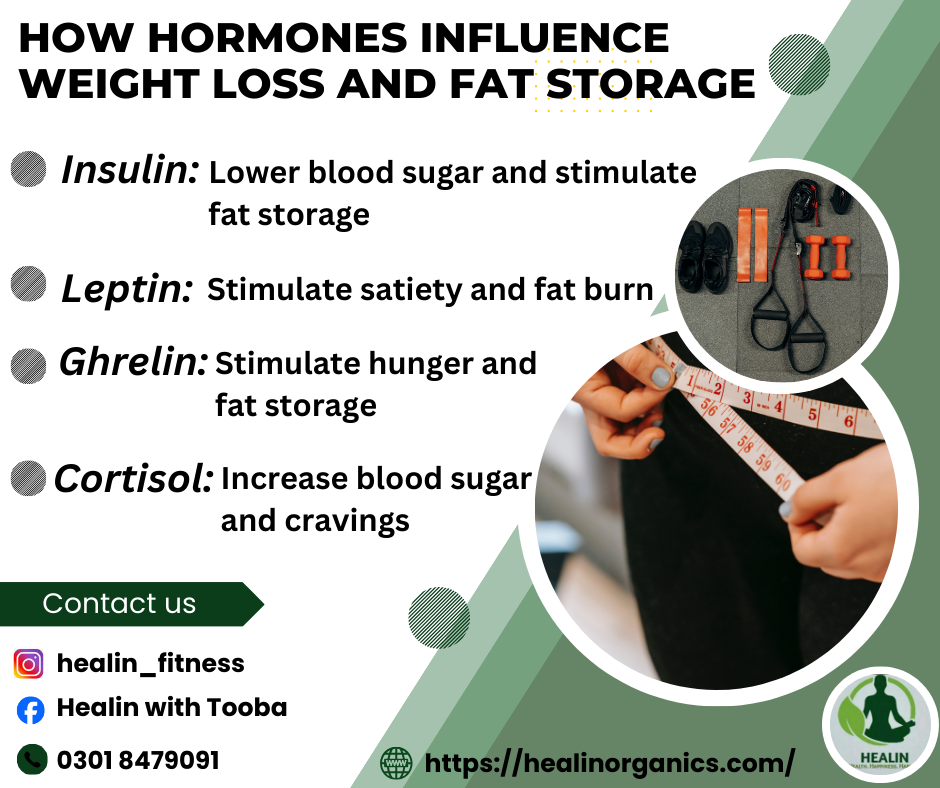
In the intricate dance of weight management, hormones play a pivotal role, orchestrating a symphony of signals that impact our body’s ability to shed or store fat. Understanding this hormonal interplay is crucial for anyone striving to achieve sustainable weight loss. Let’s delve into the science behind how hormones wield their influence on our body composition.
1. Insulin: The Gatekeeper of Fat Storage
Insulin, often associated with blood sugar regulation, is a key player in fat storage. High insulin levels, triggered by consuming carbohydrates, promote fat storage and inhibit fat breakdown.
To optimize weight loss, focus on a balanced diet with complex carbohydrates and lean proteins to avoid drastic spikes in insulin.
2. Leptin and Ghrelin: The Hunger Hormones
Leptin signals satiety, telling your brain you’ve had enough to eat. However, chronic overeating can lead to leptin resistance, where the signal is blunted, making weight loss challenging.
Ghrelin, on the other hand, stimulates hunger. Lack of sleep and irregular eating patterns can elevate ghrelin levels, making you more prone to overeating.
3. Cortisol: The Stress Hormone
Elevated cortisol levels, a response to chronic stress, can contribute to abdominal fat accumulation. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as meditation and regular exercise can help manage cortisol levels.
4. Thyroid Hormones: Metabolic Regulators
Thyroid hormones, specifically T3 and T4, play a crucial role in regulating metabolism. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can slow down metabolism, making weight loss more challenging.
Consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect thyroid issues, as medication and lifestyle adjustments may be necessary.
5. Estrogen and Testosterone: Gender Matters
Hormonal differences between genders influence fat distribution. Lower testosterone levels in men and imbalances in estrogen levels in women can impact weight loss.
Resistance training can boost testosterone levels in men, while women benefit from a balanced approach to exercise and nutrition.
6. Adiponectin: The Fat-Burning Hormone
Adiponectin enhances fat breakdown and improves insulin sensitivity. Regular exercise, particularly activities that build muscle, can increase adiponectin levels.
Including a mix of aerobic and strength training exercises can help optimize adiponectin function.
Conclusion:
In the intricate tapestry of weight loss, hormones act as master regulators, influencing our body’s propensity to burn or store fat. A holistic approach that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep is essential for harmonizing these hormonal influences. By understanding and respecting the cues our hormones provide, we empower ourselves to embark on a weight loss journey that aligns with our body’s natural rhythm.